Staying on top of new website design and optimization trends may feel intimidating. The technology seems like it evolves every single day so that while you're just catching up on terms like “mobile optimization” and “dynamic content," a billion new terms emerge.
Staying on top of new website design and optimization trends may feel intimidating. The technology seems like it evolves every single day so that while you're just catching up on terms like “mobile optimization” and “dynamic content," a billion new terms emerge.
To help you conquer the fast-paced world of website optimization, we compiled the essential terms you'll need to know as a marketer. Whether experimentation and optimization is your day job or you just are interested in how smart inbound marketers convert leads, check out the following glossary. And, if you have any terms to add, feel free to leave us a comment with the word and its definition.
For your convenience, you can jump to a letter you want by clicking on the letters below:
A B C D E F H I L M P R V W
A
A/B Testing: A/B testing, also known as split testing, is one of the most effective ways to make measurable (and scientific) improvements to your website. This practice creates two (or more) versions of a piece of content, such as a headline or call-to-action (CTA) button, and shows each version to a different, yet similarly sized audience to discover which test has a better response.
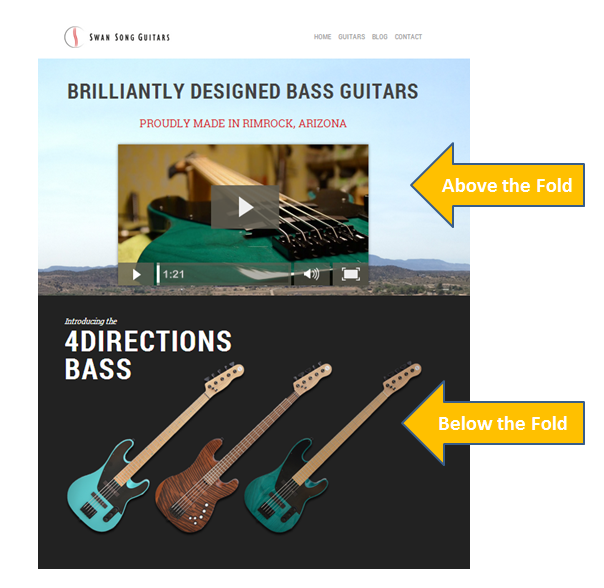
Above the Fold: This website design term is a legacy from printed newspaper days. “Above the fold” describes the part of a web page that the visitor can see without scrolling, and is usually considered the most important real estate on your page.
Below, you can see a screen shot of the Swan Song Guitars site, zoomed out to show the page elements located above and below the fold:
Anxiety Elements: From an optimization perspective, anxiety elements are parts of a web page that create anxiety for your visitors and reduce their inclination to convert on your page. For example, the line of a landing page form that asks for an email address is an element that could create anxiety, as someone might wonder how you would use his or her address. You can counteract your visitors' anxiety by adding certain page elements, such as a “privacy policy” link.
B
Bounce Rate: The bounce rate of a page is the percentage of people who left your website after viewing that page. A page with a high bounce rate is performing poorly. Comparing your high bounce pages to your low bounce pages is a great way to find out what’s working for your visitors and what isn’t.
C
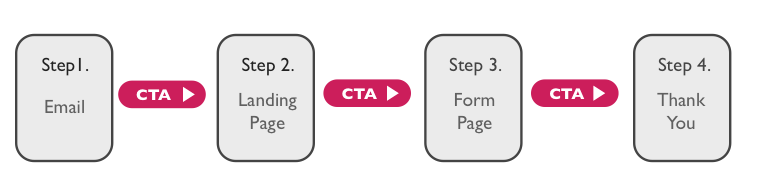
Call-to-Action (CTA): A call-to-action is a text link, button, image, or some other type of web link that encourages a website visitor to take an action on that website, such as visiting a landing page to download a piece of content.
Below is an example from Collaborate.com, which includes two distinct CTA buttons in the top navigation of its website.

Clickthrough Rate (CTR): The clickthrough rate is the percentage of your audience that advances (or, clicks through) from one part of your website to the next step of your marketing campaign. As a mathematic equation, it’s the total number of clicks that your page or CTA receives divided by the number of opportunities that people had to click (ex: number of pageviews, emails sent, etc).
Cookie: A cookie is a piece of data that a website stores in a visitor’s browser to track that visitor’s browsing history on your website. It's also a crucial component of the technology behind personalization.
Conversion: A conversion happens when your site visitor completes the goal of your individual page, such as clicking a CTA button or making a purchase. Depending on your web page and business model, you may define a conversion differently -- it could be anything from filling out a lead form to downloading an ebook to purchasing a product.
Conversion Path: The conversion path is the step-by-step series of clicks that a visitor goes through on your website, from their first interaction with you to whatever goal you’re trying to accomplish on your site. Called a conversion -- hence the term conversion path -- this goal is usually something like a form completion or a transaction.
Here's one example of a conversion path from Content Verve, though your site conversion path could branch in a variety of ways depending on your business model (e.g. you might add a shopping cart and thank you page).
Conversion Rate: The conversion rate of a page is the percentage of people who completed a desired action on a single page, such as filling out a form. Pages with high conversion rates are performing well, and pages with low conversion rates are performing poorly.
Conversion Rate Optimization (CRO): Conversion Rate Optimization is the process of improving your site conversion using design techniques, key optimization principles, and testing.
D
Dynamic Content: Dynamic content (also called as "smart content" or "adaptive content") is a term for the aspects of a website, ad, or email body that change based on the past behavior of the viewer. It creates an experience that's customized specifically for the visitor or reader at that moment. One of the most well known examples of smart content is Amazon's recommendation engine.
E
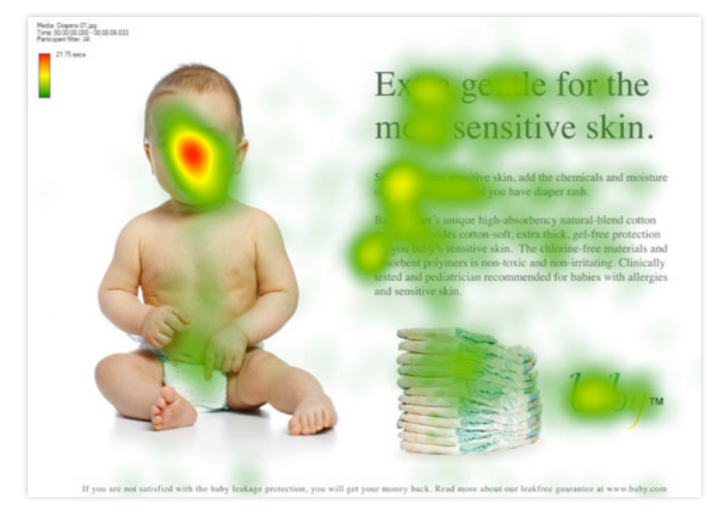
Eyetracking: Eyetracking is a form of website testing that follows eye movements of experiments' participants to gauge how they interact with web pages. This provides insight into the most important real estate on your pages.
Here is an example from The Essential Elements of High Converting Landing Pages that shows an eyetracking test.
F
Form: A form is the place your page visitors will supply information in exchange for your offer. It’s also how those visitors can convert into precious sales leads. As a best practice, only ask for information you need from your leads in order to effectively follow up with and/or qualify them.
Friction: Friction is any element of your website that is confusing, distracting, or causes stress for visitors, causing them to leave your page. Examples of friction-causing elements include dissonant colors, too much text, distracting website navigation menus, or landing page forms with too many fields.
H
Homepage: Your company homepage is an online ambassador for your brand. In contrast to a single-purpose landing page, your company homepage could serve a number of different purposes, including introducing your value proposition, establishing your brand, or recruiting new hires.
I
Incentive: An incentive is an element you add to your page that stimulates the visitor to convert. In optimization circles, online incentives are used to overcome the friction on the page. Examples include a visual that reinforces the value of your offer, or a free trial or cost calculator you offer in exchange for downloading a report or taking a survey.
Iterative Testing: Iterative testing is a process for testing your marketing campaigns where each lesson builds on previous ones to provide more insight into your customer base. While conducting one-off tests on different marketing components is possible (e.g. a single product page or new CTA button), it is far more effective to map out this kind of formal, long-term testing strategy.
L
Landing Page: Literally the page where your prospects “land” on your website, a landing page also must exist to collect a visitor’s information through a form.
Landing Page Optimization: Landing Page Optimization is the process by which companies work to optimize their landing pages using design techniques, key optimization principles, and testing. This is also sometimes called Website Optimization or Conversion Rate Optimization.
Latent Conversion: A latent conversion is a type of conversion that takes place after your visitor’s initial visit. For example, someone may look for a price matrix, leave your page to think about it, come back to your website two days later, and then make a purchase.
Lead: A lead is a person who has in some way, shape, or form indicated interest in your company's product or service.
Lifecycle Stage: Lifecycle stage refers to the your leads' current stages in their buyer decision-making process. Is this their first visit? Are they ready to buy? Are they still evaluating options? There are three main lifecycle stages:
- Awareness: Leads have either become aware of your product or service, or they have become aware that they have a need that must be fulfilled.
- Evaluation: Leads are aware that your product or service could fulfill their need, and they are trying to determine whether you are the best fit.
- Purchase: Leads are ready to make a purchase.
Long tail keyword: A long tail keyword is a very targeted search phrase that contains three or more words. It often contains a head term, which is a more generic search term, plus one or two additional words that refine the search term. For example:
- Head term: unicorn
- Long tail keywords: unicorn games online, unicorn costumes for kids, unicorn videos on youtube
Long tail keywords are more specific, which means visitors that land on your website from a long tail search term are more qualified, and consequently, more likely to convert.
M
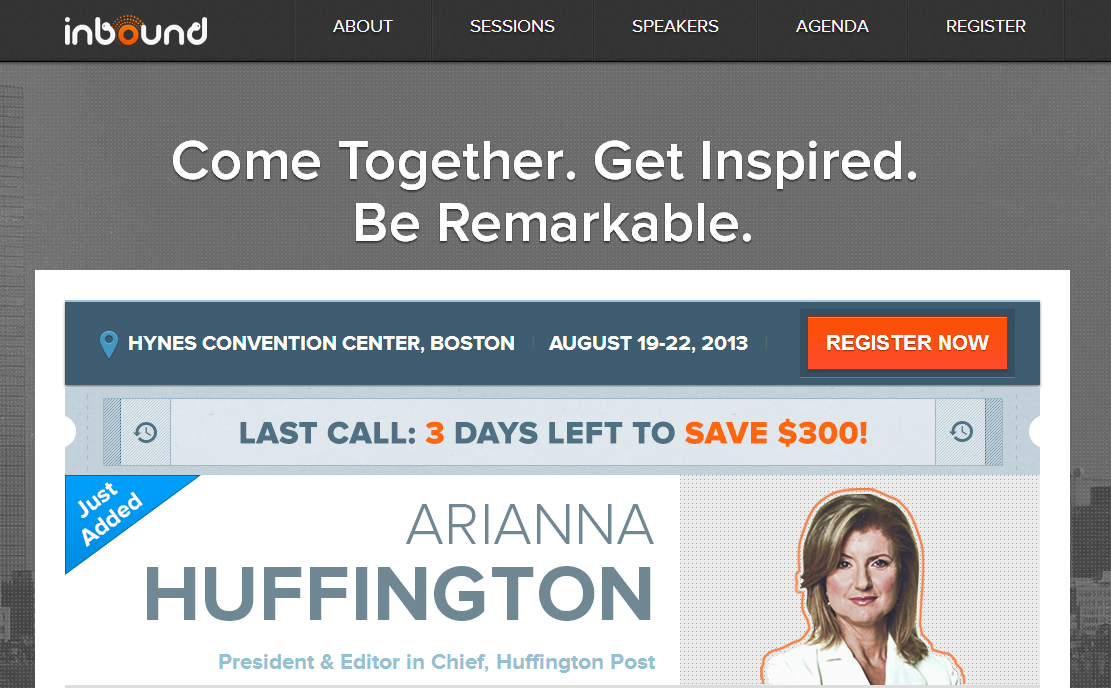
Microsite: A microsite is a cross between a landing page and a “regular” website. Microsites are used when marketers want to create a different online experience for their audience separate from their main website. These sites often have their own domain names and distinct visual branding.
Here is an example of a HubSpot microsite for our INBOUND conference. As you can see the site has similar branding to the main HubSpot homepage, but creates a distinct experience for this specific event.
Mobile Optimization: Mobile optimization means designing and formatting your website so that it’s easy to read and navigate from a mobile device. This can be done by either creating a separate mobile website or incorporating responsive design in initial site layout.
Motivation: For optimization, motivation refers to the user’s desire for your product or service. It's considered by website optimization experts, such as MarketingSherpa, as most important factor in determining a high conversion rate.
Multivariate Test: A multivariate test evaluates a number of different page elements on a web page simultaneously, in contrast to A/B testing, which compares the success of variations of one element. For example, a multivariate test may test three different images, two CTA buttons, and two headlines in an effort to find the page combination that performs best. An A/B test, on the other hand, would test two different images on one page, leaving all other variables constant. Because multivariate tests can be complicated and require significant traffic, they are generally reserved for more advanced marketing testers.
This image from Search Engine Land and Yam Designs illustrates what a multivariate tests looks like in action:

P
Personalization: Personalization is a means of targeting your audience, so that each web page or email message appears to have been created specifically for a single person. Examples of personalization include adding a name to an email subject line, showing products based on the visitor’s past purchase history, or surfacing dynamic images based on location or industry. With personalization, a visitor in New York would see a Yankees hat offer while one in Boston would be offered a picture of a Red Sox hat.
R
Responsive Design: Responsive web design is an approach to designing websites. Instead of building a separate, distinct website for each specific device it could be viewed on, the site recognizes the device that your visitor is using and automatically generates a page that is responsive to the device the content is being viewed on -- making websites always appear optimized for screens of any dimension.
To understand the difference, here is an example of the Surf Right Project’s responsive site, where you can see subtle differences between the desktop, iPad and mobile phone views.

V
Value Exchange: The value exchange is the process by which your website promotes something of value in order to get information from your visitors. For example exchanging a thought leadership ebook for personal contact information would be an online value exchange.
W
Website Optimization: Website Optimization, also sometimes called Landing Page Optimization or Conversion Rate Optimization is the process by which companies work to improve their websites using design techniques, optimization principles, and experimentation.
These are just a few website optimization terms that marketers should know. What terms would you add to this list?
Hay que tener cuidado con lo que se dice, pero más con lo que se siente!! :)